CUET is a new form of entrance examination for admission to Central Universities. This entrance examination will be conducted by the NTA (National Testing Agency), and many prestigious universities are a part of it, including Delhi University, Banaras Hindu University, University of Jharkhand, University of Allahabad, and Central University of Gujarat, and other Central Universities.
In this article by CUET Gurukul, we will tell you everything related to the Mathematics paper at the Undergraduate level of CUET, that is, the syllabus, question pattern, books to prepare from, and preparation techniques for the entrance exam.
About The Paper
Mathematics is the study of discovering and demonstrating the characteristics of various entities by pure reasoning. The discipline is primarily concerned with numbers, formulae, associated structures or algebra, forms and the spaces in which they exist, calculus, and analysis. The subject is exceedingly significant, and it is widely employed in medical science and in scientific modelling. Mathematics is also widely employed in a variety of sectors, including natural sciences, engineering, finance, computer science, and many more..
Topics of Mathematics for CUET Examination
The syllabus of Mathematics for CUET Examination is solely based on the NCERT syllabus and the examination will evaluate the fundamental knowledge so the candidates. The topics of Mathematics examination are as follows:
There will be two sections in the examination. Section A will consist of the following topics:
SECTION-A
- Algebra: The first unit will consist of the following topics: (i) Matrices and types of Matrices (ii) Equality of Matrices, transpose of a Matrix, Symmetric and Skew Symmetric Matrix (iii) Algebra of Matrices (iv) Determinants (v) Inverse of a Matrix (vi) Solving of simultaneous equations using Matrix Method.
- Calculus: The second will consist of the following topics: (i) Higher order derivatives (ii) Tangents and Normals (iii) Increasing and Decreasing Functions (iv). Maxima and Minima.
- Integration and Its Applications: The third unit will consist of the following topics: (i) Indefinite integrals of simple functions (ii) Evaluation of indefinite integrals (iii) Definite Integrals (iv). Application of Integration as area under the curve.
- Differential Equations: The fourth unit will consist of the following topics: (i) Order and degree of differential equations (ii) Formulating and solving of differential equations with variable separable.
- Probability Distributions: The fifth unit will consist of the following topics: (i) Random variables and its probability distribution (ii) Expected value of a random variable (iii) Variance and Standard Deviation of a random variable (iv). Binomial Distribution.
- Linear Programming: The sixth unit will consist of the following topics: (i) Mathematical formulation of Linear Programming Problem (ii) Graphical method of solution for problems in two variables (iii) Feasible and infeasible regions (iv). Optimal feasible solution.
Section B will be broken down into two parts, that is, Section B1 and Section B2
SECTION B1: Mathematics
- Relations and Functions: The first unit will consist of the following topics:
- Relations and Functions— Types of relations: Reflexive, symmetric, transitive and equivalence relations. One to one and onto functions, composite functions, inverse of a function. Binary operations.
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions— Definition, range, domain, principal value branches. Graphs of inverse trigonometric functions. Elementary properties of inverse trigonometric functions.
- Algebra: The second unit will consist of the following topics:
- Matrices— Concept, notation, order, equality, types of matrices, zero matrix, transpose of a matrix, symmetric and skew symmetric matrices. Addition, multiplication and scalar multiplication of matrices, simple properties of addition, multiplication and scalar multiplication. Non-commutativity of multiplication of matrices and existence of non-zero matrices whose product is the zero matrix ( restrict to square matrices of order 2 ). Concept of elementary row and column operations. Invertible matrices and proof of the uniqueness of inverse, if it exists;(Here all matrices will have real entries).
- Determinants— Determinant of a square matrix ( up to 3 × 3 matrices), properties of determinants, minors, cofactors and applications of determinants in finding the area of a triangle. Adjoint and inverse of a square matrix. Consistency, inconsistency and number of solutions of system of linear equations by examples, solving system of linear equations in two or three variables (having unique solution) using inverse of a matrix.
- Calculus: The third unit will consist of the following topics:
- Continuity and Differentiability— Continuity and differentiability, derivative of composite functions, chain rule, derivatives of inverse trigonometric functions, derivative of implicit function. Concepts of exponential, logarithmic functions. Derivatives of log x and e x .Logarithmic differentiation. Derivative of functions expressed in parametric forms. Second-order derivatives. Rolle’s and Lagrange’s Mean Value Theorems( without proof ) and their geometric interpretations.
- Applications of Derivatives— Applications of derivatives: Rate of change, increasing / decreasing functions, tangents and normals, approximation, maxima and minima ( first derivative test motivated geometrically and second derivative test given as a provable tool).Simple problems ( that illustrate basic principles and understanding of the subject as well as real-life situations). Tangent and Normal.
- Integrals: Integration as inverse process of differentiation. Integration of a variety of functions by substitution, by partial fractions and by parts, only simple integrals of the type to be evaluated:
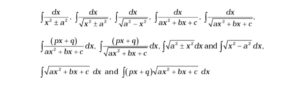
And, Definite integrals as a limit of a sum. Fundamental Theorem of Calculus ( without proof ). Basic properties of definite integrals and evaluation of definite integrals.
- Applications of the Integrals: The fourth unit will consist of the following topics: Applications in finding the area under simple curves, especially lines, arcs of circles/ parabolas/el-lipses ( in standard form only ), area between the two above said curves( the region should be clearly identifiable ).
- Differential Equations: The fifth unit will consist of the following topics: Definition, order and degree, general and particular solutions of a differential equation. Formation of differential equation whose general solution is given. Solution of differential equations by method of separation of variables, homogeneous differential equations of first order and first degree. Solutions of linear differential equation of the type –
dy/dx+ Py = Q, where P and Q are functions of x or constant.
dx/dy+ Px = Q, where P and Q are functions of y or constant. - Vectors and Three Dimensional Geometry: The fourth unit will consist of the following topics:
- Vectors— Vectors and scalars, magnitude and direction of a vector. Direction cosines/ratios of vectors. Types of vectors ( equal, unit, zero, parallel and collinear vectors ), position vector of a point, negative of a vector, components of a vector, addition of vectors, multiplication of a vector by a scalar, position vector of a point dividing a line segment in a given ratio. Scalar ( dot ) product of vectors, projection of a vector on a line. Vector( cross ) product of vectors, scalar triple product.
- Three Dimensional Geometry— Direction cosines / ratios of a line joining two points. Cartesian and vector equation of a line, coplanar and skew lines, shortest distance between two lines. Cartesian and vector equation of a plane. Angle between (i) Two lines,(ii) Two planes,(iii) A line and a plane. Distance of a point from a plane.
- Linear Programming: The fifth unit will consist of the following topics: Introduction, related terminology such as constraints, objective function, optimization, different types of linear programming ( L.P. ) problems, mathematical formulation of L. P. problems, graphical method of solution for problems in two variables, feasible and infeasible regions, feasible and infeasible solutions, optimal feasible solutions ( up to three non-trivial constrains ).
- Probability: The sixth unit will consist of the following topics: Multiplications theorem on probability. Conditional probability, independent events, total probability, Baye’s theorem. Random variable and its probability distribution, mean and variance of haphazard variable. Repeated independent( Bernoulli )trials and Binomial distribution.
SECTION B2: Applied Mathematics
- Numbers, Quantification and Numerical Application: The first unit will consist of the following topics:
- Modulo Arithmetic— Define modulus of an integer; Apply arithmetic operations using modular arithmetic rules.
- Congruence Modulo— Define congruence modulo; Apply the definition in various problems.
- Allegation and Mixture— Understand the rule of allegation to produce a mixture at a given price; Determine the mean price of a mixture; Apply rule of allegation.
- Numerical Problems— Solve real life problems mathematically.
- Boats and Streams— Distinguish between upstream and downstream; Express the problem in the form of an equation.
- Pipes and Cisterns— Determine the time taken by two or more pipes to fill or.
- Races and Games— Compare the performance of two players w.r.t. time; distance taken /distance covered / Work done from the given data.
- Partnership— Differentiate between active partner and sleeping partner; Determine the gain or loss to be divided among the partners in the ratio of their investment with due consideration of the time volume/ surface area for solid formed using two or more shapes.
- Numerical Inequalities— Describe the basic concepts of numerical inequalities; Understand and write numerical inequalities.
- Algebra: The second unit consists of the following topics:
- Matrices and Types of Matrices— Define matrix; Identify different kinds of matrices.
- Equality of matrices, Transpose of a matrix, Symmetric and Skew symmetric matrix— Determine equality of two matrices; Write transpose of given matrix; Define symmetric and skew symmetric matrix.
- Calculus: The third unit will consist of the following topics:
- Higher Order Derivatives— Determine second and higher order derivatives; Understand differentiation of parametric functions and implicit functions Identify dependent and independent variables.
- Marginal Cost and Marginal Revenue Using Derivatives— Define marginal cost and marginal revenue; Find marginal cost and marginal revenue.
- Maxima and Minima— Determine critical points of the function; Find the point(s) of local maxima and local minima and corresponding local maximum and local minimum values; Find the absolute maximum and absolute minimum value of a function.
- Probability Distributions: The fourth unit will consist of the following topics:
- Probability Distribution— Understand the concept of Random Variables and its Probability Distributions; Find probability distribution of discrete random variable.
- Mathematical Expectation— Apply arithmetic mean of frequency distribution to find the expected value of a random variable.
- Variance— Calculate the Variance and S. D. of a random variable.
- Index Numbers and Time Based Data: The fifth unit will consist of the following topics:
- Index Numbers— Define Index numbers as a special type of average.
- Construction of Index Numbers— Construct different type of index numbers.
- Test of Adequacy of Index Numbers— Apply time reversal test.
- Index Numbers and Time Based Data: The sixth unit will consist of the following topics:
- Population and Sample— Define Population and Sample; Differentiate between population and sample; Define a representative sample from a population.
- Parameter and Statistics and Statistical Interferences— Define Parameter with reference to Population; Define Statistics with reference to Sample; Explain the relation between Parameter and Statistic; Explain the limitation of Statistic to generalize the estimation for population; Interpret the concept of Statistical Significance and Statistical Inferences; State Central Limit Theorem; Explain the relation between Population-Sampling Distribution-Sample.
- Index Numbers and Time Based Data: The seventh unit will consist of the following topics:
- Time Series— Identify time series aschrono logical data.
- Components of Time Series— Distinguish between different components of time series.
- Time Series Analysis For Unvariable Data— Solve practical problems based on statistical data and Interpret.
- Financial Mathematics: The eighth unit will consist of the following topics:
- Perpetuity, Sinking Funds— Explain the concept of perpetuity and sinking fund; Calculate perpetuity; Differentiate between sinking fund and savings account.
- Valuation of Bonds— Define the concept of valuation of bond and related terms; Calculate value of bond using present value approach.
- Calculation of EMI— Explain the concept of EMI; Calculate EMI using various methods.
- Linear Method Of Depreciation— Define the concept of linear method of Depreciation; Interpret cost, residual value and useful life of an asset from the given information; Calculate depreciation.
- Linear Programming: The ninth unit will consist of the following topics:
- Introduction and Related Terminology— Familiarize with terms related to Linear Programming Problem.
- Mathematical formulation of Linear Programming Problem— Formulate Linear Programming Problem.
- Different Types of Linear Programming Problems— Identify and formulate different types of Linear Programming Problems.
- Graphical Method of Solution for problems in two Variables—Draw the Graph for a system of linear inequalities involving two variables and to find its solution graphically.
- Feasible and Infeasible Regions— Identify feasible, infeasible and bounded regions.
- Feasible and Infeasible Solutions, Optimal Feasible Solution— Understand feasible and infeasible solutions; Find optimal feasible solution.
Question Pattern of the Examination
In the CUET Mathematics examination, the question paper will be divided in two sections comprising of Section A which will comprise of 15 marks and it will cover topics of Mathematics or Applied Mathematics which will be compulsory for all candidates. Section B will consist of two sub-sections comprising of Section B1 and Section B2 where each sub-section will have 35 questions and in both sections candidates have to attempt 25 questions from Section B1 and Section B2, that is, a total of 50 questions.
Suggested Books To Prepare From
The CUET examination is strictly based on NCERT; therefore, students can take help from the following books:
- Mathematics NCERT Part 1 and 2 Class 12
- R. D. Sharma Mathematics Class 12
- CBSE All in One Mathematics Class 12
Important Tips to Prepare for Mathematics Examination of CUET
These tips and advice would help the appearing candidates to prepare for the CUET examination and help them ace the examination:
- Study From The First Day: Many students believe that Mathematics is a subject that can be covered at the last minute simply by looking at the concepts and formulas; it is wrong, and even though students have studied the same topics in school but in CUET, it will be no good for the candidates. Students must prepare and practise from the first day so that they can understand and master each topic perfectly.
- Remember the Formulas: The key to scoring well in mathematics is to remember every formula, because if the candidate knows which formula he/ she has to use, then all they have to do is put in the numbers in the slots of the formula and solve it. The candidate can remember the formulas by writing it in a separate copy or they can write down the formulas before starting a new topic.
- Take Breaks While Studying: It is extremely important to study whole heartedly and studying with full concentration for a couple of hours would be extremely beneficial. However, the candidate must take breaks after fixed intervals else they will be too stressed, and not taking breaks would take a toll on the student as he/ she will slowly get frustrated and have difficulty understanding the topics.
- Revision: Once the student has completed his/ her syllabus, they should try to revise the syllabus at least twice, and they need to revise from every corner of the book so that they can make sure they have not missed out on any important section of the topic. They must make sure that they are revising all their books, notes, and materials that they made prior to the examination. Students must make a sound revision plan that will help them to revise the syllabus effectively and efficiently.
- Solve Sample Papers and Test Series: In order to understand the question pattern of the examination, the candidates should solve as many sample papers as possible because there is a difference between the level of questions. Moreover, solving question papers and giving test series would help the students to discover their strengths and weaknesses, and they will study accordingly.
- Clearing Doubts: It is understandable that when students are solving so many question papers, they will have doubts in the complex topics. Aspirants must make a time slot for clearing their doubts, and they must get their doubts solved. The candidates must not leave any doubt because even the slightest hesitation can cause a massive setback.



